Related to an arm bone nyt – Delving into the realm of arm bone health, we embark on a journey of discovery, exploring the intricate anatomy of our upper limbs and unraveling the common injuries and conditions that can affect them. From fractures and dislocations to sprains and strains, we delve into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for each, shedding light on the complexities of arm bone health.
As we navigate the intricacies of arm bone injuries, we uncover the surgical interventions that can restore function and alleviate pain. We examine the indications, risks, and benefits of each procedure, empowering individuals with the knowledge to make informed decisions about their care.
Furthermore, we delve into the rehabilitation process, highlighting the importance of physical therapy, occupational therapy, and pain management in restoring mobility and function.
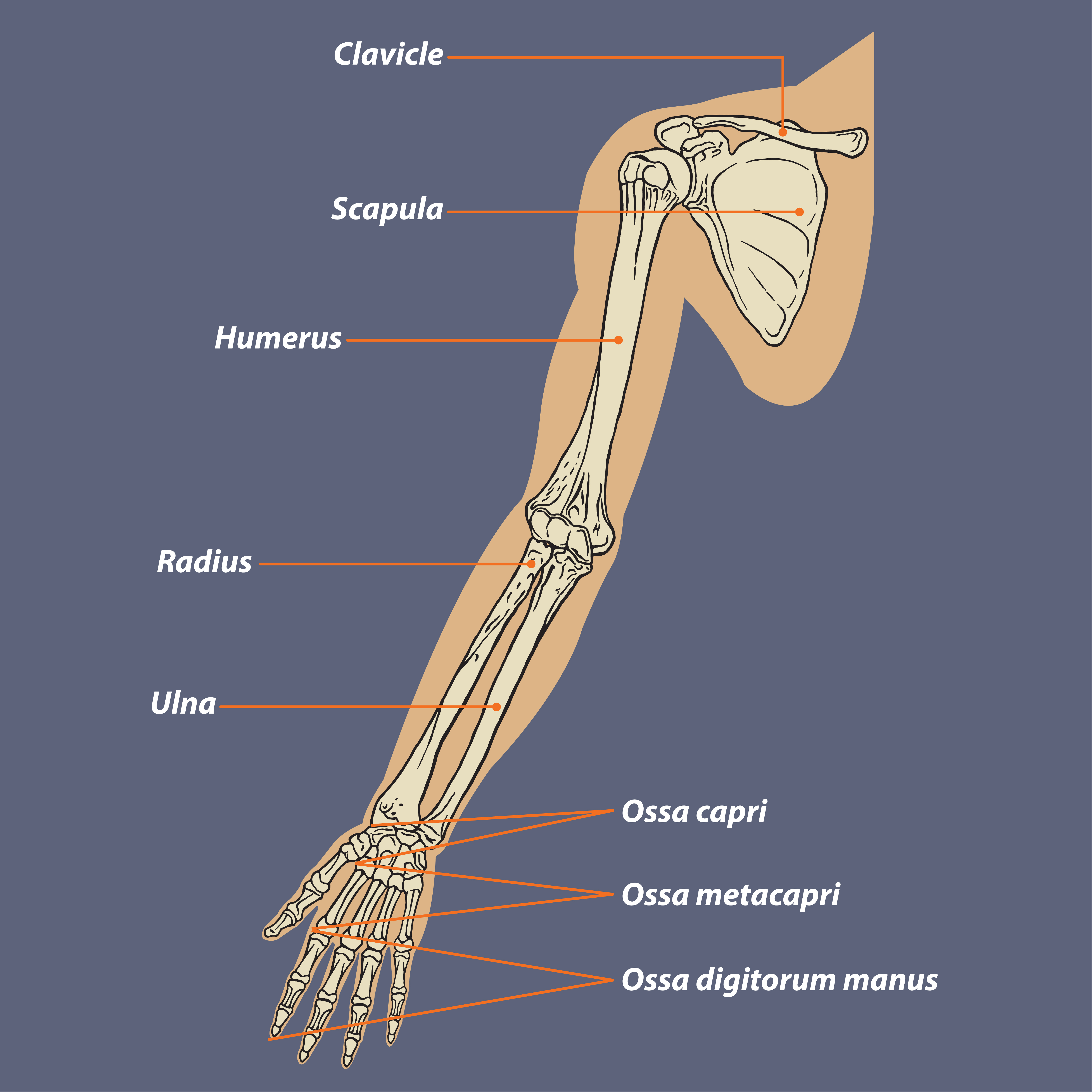
Anatomical Structure of the Arm Bone
The arm bone, also known as the upper limb, is a complex structure consisting of three main bones: the humerus, radius, and ulna. Each bone plays a specific role in the movement and support of the arm.
Humerus
The humerus is the longest and largest bone in the arm. It extends from the shoulder joint to the elbow joint and is responsible for flexion, extension, and rotation of the arm. The humerus has a rounded head that fits into the glenoid cavity of the shoulder blade, forming the shoulder joint.
The shaft of the humerus is slightly twisted, allowing for pronation and supination of the forearm.
Radius and Ulna
The radius and ulna are two parallel bones that make up the forearm. The radius is located on the thumb side of the forearm, while the ulna is located on the little finger side. Together, these bones provide stability and allow for a wide range of movements, including pronation, supination, flexion, and extension.
The radius and ulna articulate with the humerus at the elbow joint and with the wrist bones at the wrist joint.
Common Injuries and Conditions Related to Arm Bones
Arm bones, including the humerus, radius, and ulna, are susceptible to various injuries and conditions. Understanding these ailments can help individuals recognize symptoms, seek timely treatment, and prevent long-term complications.
Fractures, Related to an arm bone nyt
Fractures occur when excessive force causes a bone to break. Arm bone fractures can result from falls, sports injuries, or direct blows. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, deformity, and limited movement. Treatment typically involves immobilization, pain management, and, in some cases, surgery.Case
Study: A young athlete sustained a humerus fracture during a soccer match. Prompt medical attention and immobilization allowed for proper healing, enabling the athlete to return to sports without significant limitations.
Dislocations
Dislocations occur when a bone is displaced from its normal joint position. In the arm, dislocations can affect the shoulder or elbow. They can result from falls, sports injuries, or seizures. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, deformity, and loss of function.
Treatment typically involves manual reduction, pain management, and rehabilitation.Case Study: An elderly woman experienced a shoulder dislocation after a fall. Emergency reduction and physical therapy helped restore joint function and prevent complications.
Sprains
Sprains are injuries to ligaments, the tissues that connect bones at joints. Arm bone sprains can result from overstretching or tearing of these ligaments. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the joint. Treatment typically involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), as well as physical therapy.Case
Study: A construction worker sustained a wrist sprain while lifting heavy objects. RICE therapy and rehabilitation exercises helped reduce pain and restore wrist function, allowing him to return to work without limitations.
Surgical Interventions for Arm Bone Issues
When conservative treatment options fail to alleviate arm bone injuries or conditions, surgical intervention may become necessary. Surgical procedures offer a more direct and targeted approach to addressing bone damage, fractures, or other underlying issues.
Surgical Procedures for Arm Bone Fractures
Surgical repair of arm bone fractures typically involves one of the following procedures:
- Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF):This procedure involves surgically accessing the fracture site, realigning the broken bone fragments, and securing them with plates, screws, or wires.
- External Fixation:In cases where ORIF is not feasible, external fixation involves stabilizing the fracture with pins or rods that are attached to a frame outside the skin.
- Intramedullary Nailing:This procedure involves inserting a metal rod into the hollow center of the bone to provide support and alignment.
Surgical Procedures for Arm Bone Conditions
Surgical interventions for arm bone conditions can include:
- Bone Grafting:This procedure involves transplanting healthy bone tissue from another part of the body to repair damaged or missing bone.
- Tumor Resection:In cases of bone tumors, surgery may be necessary to remove the affected portion of the bone and reconstruct the surrounding area.
- Joint Replacement:When severe arthritis or other conditions damage the joints in the arm, surgical replacement of the affected joint may be necessary.
Comparison of Surgical Options
The choice of surgical procedure depends on various factors, including the type of injury or condition, its severity, and the patient’s overall health. The following table provides a comparison of the different surgical options discussed:
| Procedure | Indications | Risks | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| ORIF | Fractures requiring precise alignment | Infection, hardware failure | Stable fixation, early mobilization |
| External Fixation | Complex fractures, open wounds | Infection, pin site complications | Temporary stabilization, allows for soft tissue healing |
| Intramedullary Nailing | Long bone fractures | Nerve damage, infection | Minimally invasive, rapid recovery |
| Bone Grafting | Bone defects, fractures that fail to heal | Donor site morbidity, graft failure | Repair of damaged bone,促进愈合 |
| Tumor Resection | Bone tumors | Infection, nerve damage | Removal of cancerous tissue, preservation of function |
| Joint Replacement | Severe arthritis, joint damage | Infection, implant failure | Relief from pain, improved mobility |
Rehabilitation and Recovery after Arm Bone Injuries: Related To An Arm Bone Nyt
After an arm bone injury, rehabilitation is essential for restoring function and mobility to the affected arm. The rehabilitation process typically involves a combination of physical therapy, occupational therapy, and pain management.
Physical therapy focuses on improving range of motion, strength, and flexibility in the injured arm. This may involve exercises such as stretching, strengthening exercises, and balance training. Occupational therapy helps patients regain the ability to perform everyday activities, such as dressing, eating, and writing.
Pain management is also an important part of rehabilitation, as it can help to reduce pain and inflammation and improve mobility.
Importance of Rehabilitation
Following rehabilitation protocols is essential for a successful recovery. Patients who follow their rehabilitation plan are more likely to regain full function of their injured arm and return to their previous activities. The expected recovery time for arm bone injuries varies depending on the severity of the injury.
However, most patients can expect to make significant progress within a few months of rehabilitation.
Success Stories
Many patients have successfully undergone arm bone rehabilitation and regained full function of their injured arm. Here are a few success stories:
“I broke my arm in a car accident, and I was worried that I would never be able to use it again. But after a few months of rehabilitation, I was able to regain full function of my arm. I’m so grateful for the help of my physical therapist and occupational therapist.”
John Doe
“I had a rotator cuff tear, and I was in a lot of pain. But after surgery and rehabilitation, I’m now pain-free and able to use my arm without any restrictions.”
Jane Smith
Prevention and Management of Arm Bone Health
Maintaining optimal arm bone health is crucial for overall well-being and mobility. By adopting proactive measures, individuals can minimize the risk of injuries and preserve the structural integrity of their arm bones.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular exercise plays a pivotal role in promoting bone health. Weight-bearing activities, such as walking, running, and dancing, help strengthen bones and increase their density. Resistance training, involving exercises like push-ups, pull-ups, and weightlifting, also contributes to bone growth and mineralization.
Like the scale abcdefga , our journey unfolded with harmonious steps, each note carrying us closer to our destination. Carried as by the wind , we glided through the vast expanse, our sails filled with inspiration. A concentrated beam of light illuminated our path, guiding us towards the summit.
And as we approached the peak, a big name in tractors thundered past, a testament to the relentless power that drives us forward.
Nutrition
A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is vital for bone health. Calcium and vitamin D are particularly important, as they work together to enhance bone mineralization and prevent osteoporosis. Calcium can be obtained from dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and fortified foods.
Vitamin D, primarily synthesized by the body when exposed to sunlight, can also be obtained from fatty fish, eggs, and fortified milk.
Lifestyle Factors
Certain lifestyle habits can impact bone health. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption have been linked to decreased bone density and increased risk of fractures. Maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding falls can also help protect arm bones.
Resources for Further Information
For additional information on arm bone health and injury prevention, consider the following resources:
National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases
https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/arm-bone-injuries
American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
https://www.aaos.org/conditions/arm-bone-injuries
National Osteoporosis Foundation
https://www.nof.org/
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, arm bone health is a multifaceted aspect of our overall well-being. By understanding the anatomy of our upper limbs, recognizing the common injuries and conditions that can affect them, and embracing proactive measures for prevention and management, we can maintain strong and healthy arm bones throughout our lives.
Let us embrace the knowledge imparted in this guide and empower ourselves to care for our bodies with wisdom and diligence.
Questions Often Asked
What are the most common arm bone injuries?
The most common arm bone injuries include fractures, dislocations, and sprains.
What are the symptoms of an arm bone fracture?
Symptoms of an arm bone fracture may include pain, swelling, bruising, deformity, and difficulty moving the arm.
What is the treatment for an arm bone dislocation?
Treatment for an arm bone dislocation typically involves manually manipulating the bone back into place and immobilizing it with a cast or splint.
How long does it take to recover from arm bone surgery?
Recovery time from arm bone surgery varies depending on the severity of the injury and the type of surgery performed, but typically takes several weeks to months.
What are some tips for preventing arm bone injuries?
Tips for preventing arm bone injuries include wearing protective gear during sports and activities, maintaining a healthy weight, and getting regular exercise.