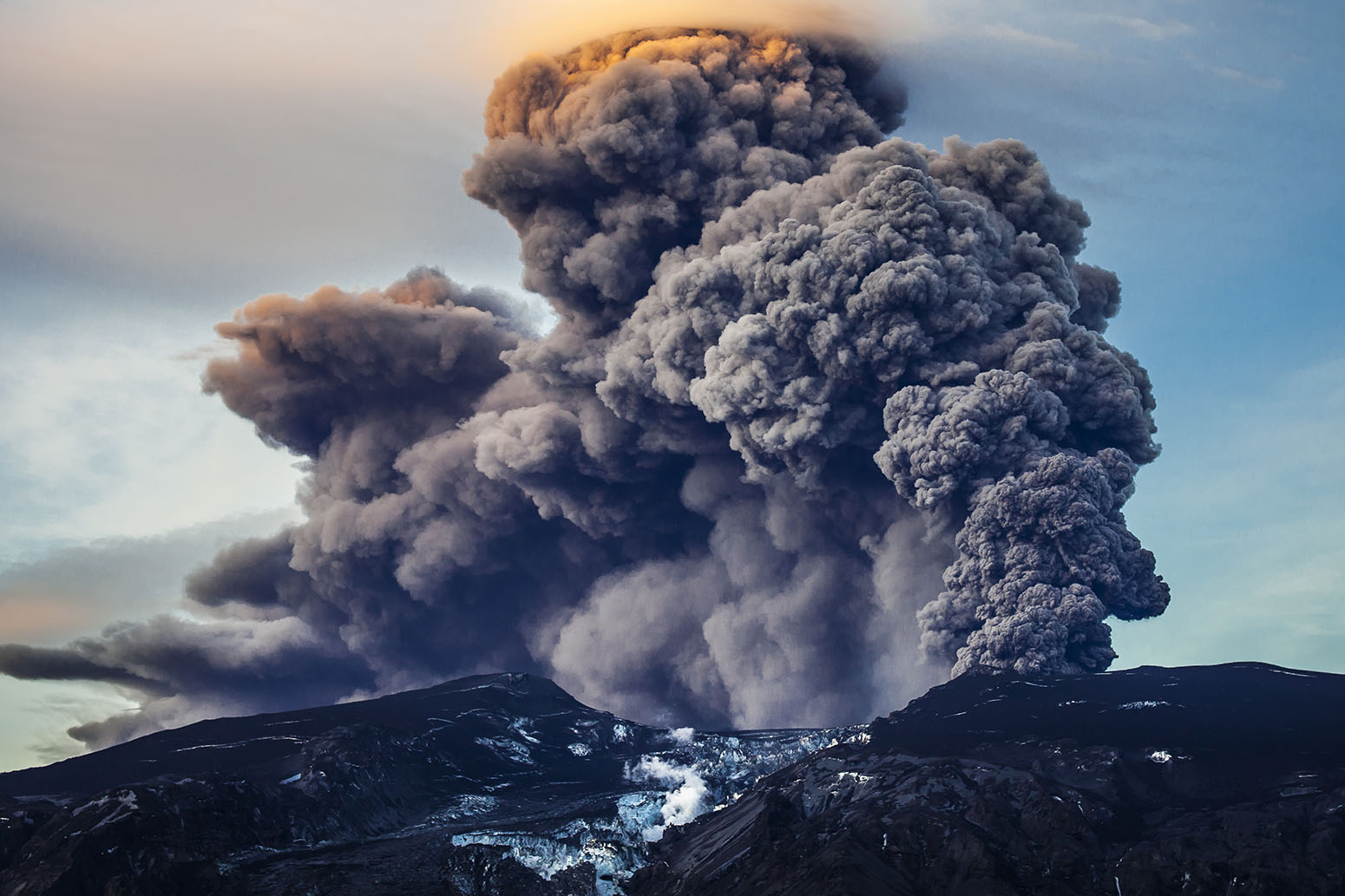
Volcanic ash dark and darker sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. As we delve into the depths of this captivating topic, we will explore the composition of volcanic ash, its profound impact on climate and environment, and its diverse applications in agriculture, construction, art, and culture.
Volcanic Ash Composition
Volcanic ash is composed of tiny rock particles and minerals that are ejected from a volcano during an eruption. It is formed when magma, or molten rock, rises to the surface of the Earth and is explosively fragmented into small pieces.
The chemical composition of volcanic ash varies depending on the type of volcanic eruption and the composition of the magma. However, in general, volcanic ash is composed of the following elements:
- Silicon (Si)
- Oxygen (O)
- Aluminum (Al)
- Iron (Fe)
- Magnesium (Mg)
- Calcium (Ca)
- Sodium (Na)
- Potassium (K)
In addition to these elements, volcanic ash can also contain trace amounts of other elements, such as titanium, manganese, and zinc.
Minerals Found in Volcanic Ash
Volcanic ash can contain a variety of minerals, including:
- Quartz
- Feldspar
- Pyroxene
- Amphibole
- Mica
- Olivine
The type of minerals found in volcanic ash depends on the composition of the magma and the temperature and pressure conditions under which the magma was formed.
Variation in Ash Composition
The composition of volcanic ash can vary depending on the type of volcanic eruption. For example, ash from explosive eruptions tends to be more felsic, or rich in silica, than ash from effusive eruptions. This is because explosive eruptions are more likely to eject magma that is high in silica content.
The composition of volcanic ash can also vary depending on the location of the volcano. For example, ash from volcanoes that are located near the ocean tends to be more mafic, or rich in iron and magnesium, than ash from volcanoes that are located inland.
This is because the magma that forms near the ocean is more likely to be contaminated with seawater, which is rich in iron and magnesium.
Impact on Climate and Environment
Volcanic ash, ejected high into the atmosphere during volcanic eruptions, plays a pivotal role in regulating the Earth’s climate and shaping its environment. Its presence in the atmosphere can have profound effects on air quality, visibility, plant and animal life, and even global temperatures.
Effects on Climate
Volcanic ash, composed primarily of tiny rock and mineral particles, acts as a reflective barrier in the atmosphere, scattering and absorbing incoming solar radiation. This can lead to a temporary cooling effect on the Earth’s surface, as less sunlight reaches the ground.
The magnitude and duration of this cooling depend on the amount and altitude of the ash cloud.
In addition, volcanic ash can trap heat within the atmosphere, contributing to global warming. The ash particles absorb infrared radiation emitted by the Earth’s surface, preventing it from escaping into space. This can lead to a gradual increase in global temperatures over time.
Effects on Air Quality and Visibility
Volcanic ash can significantly impair air quality, particularly in areas near active volcanoes. The ash particles can irritate the respiratory system, causing coughing, wheezing, and other respiratory problems. In severe cases, prolonged exposure to volcanic ash can lead to serious health issues.
Furthermore, volcanic ash can reduce visibility, making it difficult to navigate and engage in outdoor activities. The ash particles scatter light, creating a hazy or foggy atmosphere that can obstruct visibility for miles around the eruption site.
Effects on Plant and Animal Life
Volcanic ash can have both positive and negative effects on plant and animal life. On the one hand, ash can provide essential nutrients to the soil, enriching it and promoting plant growth. The minerals in the ash can also be beneficial to grazing animals, providing them with essential dietary supplements.
On the other hand, volcanic ash can also be harmful to plants and animals. The ash can block sunlight, inhibiting photosynthesis and stunting plant growth. It can also clog the gills of fish and damage the respiratory systems of birds and mammals.
Volcanic Ash in Agriculture
Volcanic ash, often perceived as a destructive force, holds remarkable benefits for agriculture. Rich in essential minerals and nutrients, it serves as a natural fertilizer, enhancing soil fertility and crop yields. However, managing volcanic ash in agricultural areas presents unique challenges, requiring careful consideration to harness its potential while mitigating its adverse effects.
Benefits of Volcanic Ash for Soil Fertility
Volcanic ash is a valuable source of essential plant nutrients, including potassium, phosphorus, calcium, and magnesium. These minerals are crucial for plant growth and development, promoting root growth, photosynthesis, and overall crop health. Additionally, volcanic ash contains trace elements like iron, zinc, and manganese, which play vital roles in enzyme function and plant metabolism.Enhancing
Soil Structure: Volcanic ash improves soil structure by increasing its porosity and water retention capacity. The porous nature of ash allows for better root penetration, aeration, and drainage, promoting healthy root development. Moreover, volcanic ash acts as a soil conditioner, reducing compaction and improving water infiltration, essential for plant growth and nutrient uptake.
Challenges Associated with Managing Volcanic Ash in Agricultural Areas
Despite its benefits, managing volcanic ash in agricultural areas can be challenging.Soil pH Modification: Volcanic ash is typically acidic, and its incorporation into soil can lower soil pH levels. This acidity can affect nutrient availability, potentially inhibiting plant growth. To mitigate this issue, farmers may need to apply lime or other soil amendments to neutralize the acidity and maintain optimal soil pH for crop production.Ash
Accumulation: Heavy ashfall can bury crops and smother vegetation, causing significant crop damage. In extreme cases, thick layers of ash can impede sunlight penetration, affecting photosynthesis and plant growth. Farmers may need to manually remove excess ash or use machinery to clear fields, which can be time-consuming and costly.Nutrient
Imbalances: While volcanic ash provides essential nutrients, it can also lead to nutrient imbalances in soil. The high levels of certain nutrients, such as potassium, can disrupt the uptake of other nutrients, affecting plant growth and yield. Farmers need to monitor soil nutrient levels and adjust fertilization practices accordingly to maintain a balanced nutrient profile.
Examples of Volcanic Ash Improving Crop Yields
Despite the challenges, volcanic ash has been successfully used to improve crop yields in various regions.In Japan, farmers have utilized volcanic ash from Mount Fuji to enhance the fertility of their rice paddies. The ash’s rich nutrient content has resulted in increased rice yields, making Japan one of the world’s leading rice producers.In
Ecuador, volcanic ash from Cotopaxi volcano has been used to improve soil fertility for potato cultivation. The ash’s high potassium content has led to increased potato yields, supporting the livelihoods of local farmers.These examples demonstrate the potential of volcanic ash as a natural fertilizer, highlighting its ability to improve soil fertility and enhance crop yields.
By carefully managing volcanic ash in agricultural areas, farmers can harness its benefits while mitigating its potential drawbacks, contributing to sustainable and productive farming practices.
Volcanic Ash in Construction
Volcanic ash, a fine-grained material produced by volcanic eruptions, possesses unique properties that make it a valuable resource in the construction industry. Its composition, consisting primarily of silica, alumina, and various minerals, provides a versatile and durable material for a range of construction applications.
Properties of Volcanic Ash, Volcanic ash dark and darker
The properties of volcanic ash that make it suitable for construction include its:
Lightweight
Volcanic ash has a low density, making it a lightweight material that can reduce the overall weight of structures.
Insulating
The porous nature of volcanic ash provides excellent thermal insulation, helping to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures and reduce energy consumption.
Fire-resistant
Volcanic ash is non-combustible and has high resistance to fire, providing an additional layer of protection for buildings.
Pozzolanic
Volcanic ash reacts with calcium hydroxide to form cementitious compounds, enhancing the strength and durability of concrete and other cementitious materials.
Types of Construction Materials
Volcanic ash can be used to produce various construction materials, including:
Concrete
Volcanic ash can be added to concrete as a partial replacement for cement, improving its strength, durability, and workability.
Mortar
Volcanic ash can be used as a binder in mortar, providing strong and durable joints for masonry structures.
Insulation
Volcanic ash can be used as a lightweight and fire-resistant insulation material for buildings and pipelines.
Soil stabilization
Volcanic ash can be mixed with soil to improve its stability and drainage properties, making it suitable for road construction and erosion control.
Historical and Modern Uses
Volcanic ash has been used in construction for centuries. The ancient Romans used volcanic ash, known as pozzolana, to build the Pantheon and other iconic structures. In modern times, volcanic ash continues to be used in construction projects around the world.
For example, the Burj Khalifa in Dubai, the tallest building in the world, incorporates volcanic ash in its concrete mix.
Volcanic Ash in Art and Culture
Volcanic ash, with its unique texture and dark hues, has captivated artists and cultures throughout history. In traditional art forms, it has been used as a pigment for cave paintings, pottery, and sculptures. Its ability to create intricate patterns and textures has made it a favorite medium for contemporary artists as well.
Cultural Significance
Volcanic ash holds deep cultural significance in many societies. In some cultures, it is believed to possess spiritual powers and is used in rituals and ceremonies. In other cultures, it is seen as a symbol of fertility and renewal, representing the transformative power of nature.
Influence on Mythology, Folklore, and Literature
Volcanic ash has also influenced mythology, folklore, and literature. In ancient Greek mythology, the ash from Mount Vesuvius was said to have buried the city of Pompeii, a legend that has been immortalized in art and literature. In some cultures, volcanic ash is associated with dragons and other mythical creatures, symbolizing the destructive yet awe-inspiring forces of nature.
Closure: Volcanic Ash Dark And Darker
In conclusion, volcanic ash dark and darker has left an indelible mark on our planet and human civilization. Its multifaceted nature has shaped landscapes, influenced cultures, and provided invaluable insights into the intricate workings of our world. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of volcanic ash, we can appreciate its unique beauty and harness its potential for sustainable development and artistic expression.
Question Bank
What are the main components of volcanic ash?
Volcanic ash is primarily composed of tiny fragments of rock, minerals, and volcanic glass.
How does volcanic ash affect air quality?
Volcanic ash can reduce visibility, irritate the respiratory system, and cause respiratory problems.
Can volcanic ash benefit agriculture?
Yes, volcanic ash can provide essential nutrients for soil and improve crop yields.
What are some historical uses of volcanic ash in construction?
Volcanic ash has been used as a building material in ancient Rome, Pompeii, and other historical structures.
How has volcanic ash influenced art and culture?
Volcanic ash has been used in traditional paintings, sculptures, and even as a canvas for contemporary art.